Blockchain technology is a shared, auditable, immutable ledger of transaction records that is distributed across a peer-to-peer network of computer systems. These immutable record keeps track of assets and builds trust in the distributed system.
- It is distributed database that keeps track of ever-increasing list of ordered transaction records, which are also known as blocks.
- In the distributed database, the blocks are linked using advance cryptography algorithms.
- All blocks consist of a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
- This help attain immutability – the transaction record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all the subsequent (previous) blocks and the shared consensus across the network.
Unlock the potential of digital assets for your institution
Public-private key cryptography
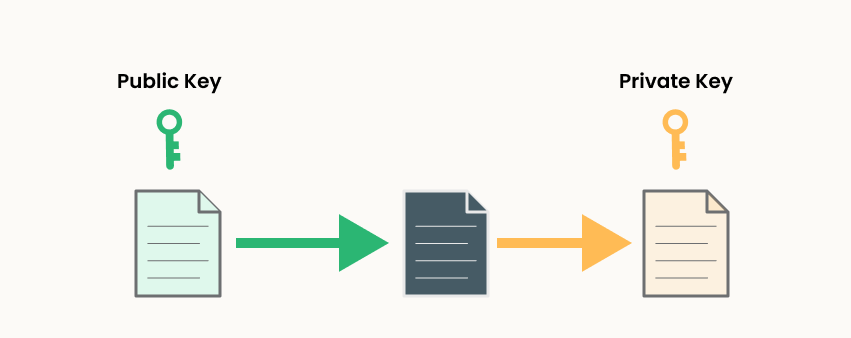
The public-private key cryptography constitutes of a pair of keys (a public key and a private key). The public key is associated with an entity (an individual or business) that needs to authenticate its identity on blockchain or to sign transaction or to encrypt transaction data. The public key is published on the chain but the corresponding private key is only known to the actual owner and kept secret. The private key is unique to every participant. The public and private keys work in unison to unlock data on the distributed ledger.
Blockchain for Business
- From a business perspective, any object of value can be transacted and tracked on the blockchain network which reduces risk and operational cost.
- Because records are immutable, there is less need for oversight.
- Blockchain enables participants to exchange valuable products directly eliminating the requirement of intermediaries.
- Additionally, on blockchain, transaction settlement time is faster, thanks to the trusted, shared, auditable ledger technology, as it doesn’t require verification or certification from a centralized authority.
- Blockchain’s security features eliminates the possibility of tampering by a bad actor.
Secure and manage your digital assets with Liminal
In hindsight, the purpose of the blockchain is to allow digital information to be recorded in a distributed manner but not be altered, deleted, changed, or destroyed.
Components of Blockchain
- Consensus mechanism is a fault-tolerant mechanism. It is employed by network of computers, where multiple agents are involved, to achieve agreement over a signal state of the network or data in a distributed fashion. It authenticates and verifies transactions across network. Proof of work, proof of stake, and practical byzantine fault tolerance BFT are three main kinds of algorithm employed to achieve consensus.
- Shared ledger is an “append-only” distributed public system. In shared ledger, the transaction record including other associated information gets recorded for only once. The role of the shared ledger is to eliminate the risk posed by duplication of records and maintain transparency across network.
- Smart contracts are self-executing contracts or programs that are stored on the blockchain network and gets automatically executed when predetermined conditions are met by both the parties involved in the transaction. The set of rules hard coded in the self-executing program governs the way business transaction work.
- Permissions help decide the level of network participation. Depending on the permissions offered, the blockchain can classified into permissioned, permissionless or hybrid. The purpose of the permissions is to authenticate and verifies network participants. It also allows enterprises to comply with the regulatory requirement especially the data protection regulations.
The Pros and Cons of Blockchain technology
Undoubtedly, the potential of blockchain technology as a form of the immutable record-keeping ledger is limitless. Unlike other technological innovations, blockchain comes with greater user privacy and heightened security protocol that helps eliminate the probability of errors.
Pros:
- Blockchain help improves accuracy by eliminating human involvement in the verification process
- Blockchain help eliminates the need for third-party entities, eventually reducing the cost
- Blockchain’s decentralized ledger makes it impossible to tamper with record entries
- On a blockchain, the transactions are secure, private, and efficient. Transparency is instilled across blockchain infrastructure
- Blockchain provides a functioning alternative for banking. It also provides a secure alternative to citizens of countries with unreliable, underdeveloped, and corrupt governments
Cons:
- Existing mining infrastructure consumes enormous amounts of electricity to compute complex verification algorithms. The transaction per second performed on the legacy blockchain is quite low.
- Not the entire blockchain ecosystem, but bitcoin has a history of involvement in illegal ac activities, especially on the dark web.
- The regulatory uncertainty is among the driving factors that are disincentivizing most investors from adopting the blockchain.
- There is a limit to the amount of information users can store on blockchain.
Did you know?
- The foundational principles of blockchain technology were first outlined in the year 1991 by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta, two well-recognized mathematicians. They aim to develop a system where document timestamps cannot get tampered at any cost.
- The computer scientist and cryptographic activist Hal Finney introduced reusable proof of work (PoW) as a prototype for digital cash in the year 2004. PoW help solves the double-spending problem by maintaining the ownership of token registered on a trusted server.
- Blockchain, as we know it today, was first proposed/ invented by an individual or a group of people – with the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. He was the first to present the original Bitcoin whitepaper, which later became the cornerstone of the existing blockchain ecosystem.
- The global blockchain market is projected to be worth $1,431.54 billion by the end of this decade. The blockchain is expected to boost global GDP by $1.76 trillion by 2030.
- As of now (the year 2022), (according to Coin Gecko) there are 12,932 active cryptocurrencies, and 552 exchanges live. The global cryptocurrency market capitalization today is around $1.05 Trillion.






